通常,我们会在自定义类型中去定义一个依赖属性,比如UserControl用户控件。
第一步,创建一个新的用户控件,取名为Widget。
第二步,我们在Widget的前端代码中进行控件布局。
<UserControl x:Class="HelloWorld.Controls.Widget"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:HelloWorld.Controls"
mc:Ignorable="d"
x:Name="userControl"
FontSize="30"
Foreground="#666666"
BorderBrush="#8CDDCD"
d:DesignHeight="450"
d:DesignWidth="800">
<Border BorderBrush="{Binding ElementName=userControl,Path=BorderBrush}">
<Border.Style>
<Style TargetType="Border">
<Setter Property="Padding" Value="10"/>
<Setter Property="Background" Value="White"/>
<Setter Property="BorderBrush" Value="#8CDDCD"/>
<Setter Property="BorderThickness" Value="0 3 0 0"/>
<Setter Property="Margin" Value="5"/>
<Style.Triggers>
<Trigger Property="IsMouseOver" Value="True">
<Setter Property="Background" Value="#F7F9F9"/>
</Trigger>
</Style.Triggers>
</Style>
</Border.Style>
<Grid>
<Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<ColumnDefinition/>
<ColumnDefinition Width="auto"/>
</Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition/>
<RowDefinition/>
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<TextBlock Grid.Row="0" Grid.Column="0" Text="{Binding Value}"
Foreground="{Binding ElementName=userControl,Path=Foreground}"
FontSize="{Binding ElementName=userControl,Path=FontSize}" />
<TextBlock Grid.Row="1" Grid.Column="0" Text="{Binding Title}"
Foreground="{Binding ElementName=userControl,Path=Foreground}"
FontSize="14" TextWrapping="Wrap"/>
<TextBlock Grid.Row="0" Grid.Column="1" Text="{Binding Icon}"
Foreground="{Binding ElementName=userControl,Path=BorderBrush}"
FontSize="26" Grid.RowSpan="2" VerticalAlignment="Center"/>
</Grid>
</Border>
</UserControl>
在这里,我们一共实例化了5个控件,最外层的Border控件用来做修饰,且它的边框颜色绑定了当前UserControl控件的边框颜色。Grid里面有3个TextBlock文字块控件,其中的前景色、字号也分别绑定了当前UserControl的属性。这样做的好处是,将来实例化这个Widget自定义用户控件时,我们就可以设置它的相关属性,从而改变内部的边框颜色、字体颜色和字体大小。
需要注意的是,3个TextBlock控件Text属性分别绑定了Value、Title、Icon三个属性,这三个属性就是我们要去自定义的依赖属性。
第三步,定义依赖属性。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Controls;
using System.Windows.Data;
using System.Windows.Documents;
using System.Windows.Input;
using System.Windows.Media;
using System.Windows.Media.Imaging;
using System.Windows.Navigation;
using System.Windows.Shapes;
namespace HelloWorld.Controls
{
/// <summary>
/// Widget.xaml 的交互逻辑
/// </summary>
public partial class Widget : UserControl
{
public Widget()
{
InitializeComponent();
DataContext = this;
}
public string Icon
{
get { return (string)GetValue(IconProperty); }
set { SetValue(IconProperty, value); }
}
public static readonly DependencyProperty IconProperty =
DependencyProperty.Register("Icon", typeof(string), typeof(Widget), new PropertyMetadata("☻"));
public string Title
{
get { return (string)GetValue(TitleProperty); }
set { SetValue(TitleProperty, value); }
}
public static readonly DependencyProperty TitleProperty =
DependencyProperty.Register("Title", typeof(string), typeof(Widget), new PropertyMetadata("请输入标题"));
public string Value
{
get { return (string)GetValue(ValueProperty); }
set { SetValue(ValueProperty, value); }
}
public static readonly DependencyProperty ValueProperty =
DependencyProperty.Register("Value", typeof(string), typeof(Widget), new PropertyMetadata("内容"));
}
}
通过在C#后端输入propdp,再按下tab键,VS会自动创建依赖属性的定义模板代码,我们只需要修改模板中的属性类型、属性名、和注册依赖属性时的相关参数即可。如上述代码所示,这里分别注册了IconProperty、TitleProperty和ValueProperty三个依赖属性,并且将它们注册到Widget类型上。由于依赖属性天生具有属性通知功能,所以我们不必去实现INotifyPropertyChanged接口,只需要将当前类做为ViewModel传给Widget的DataContent,前端的控件就可以绑定Value、Title、Icon三个属性了。
第四步,使用自定义控件
我们回到MainWindow.xaml代码中,并实例化4个Widget自定义控件。
<Window x:Class="HelloWorld.MainWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:HelloWorld" xmlns:controls="clr-namespace:HelloWorld.Controls"
mc:Ignorable="d" Background="LightGray"
Title="WPF中文网 - www.wpfsoft.com" Height="350" Width="500">
<StackPanel>
<StackPanel Orientation="Horizontal">
<controls:Widget Icon="¥"
Title="本年度销售总额"
Value="38452.21"
Width="215"
Height="100"/>
<controls:Widget Icon="◈"
Title="系统访问量"
Value="9985"
Foreground="#415767"
BorderBrush="#87BEE4"
Width="225"
Height="110"/>
</StackPanel>
<StackPanel Orientation="Horizontal">
<controls:Widget Icon="◈"
Title="系统访问量"
Value="9985"
Foreground="#495E26"
BorderBrush="#C1E487"
Width="235"
Height="120"/>
<controls:Widget Icon="㍿"
Title="日本丰田汽车国际进出口贸易有限公司"
Value="股票代码95568"
Foreground="#4E3A55"
BorderBrush="#CB87E4"
FontSize="24"
Width="245"
Height="130"/>
</StackPanel>
</StackPanel>
</Window>
在实例化Widget自定义控件后,设置依赖属性不同的值,控件就会绘制不同的呈现效果。
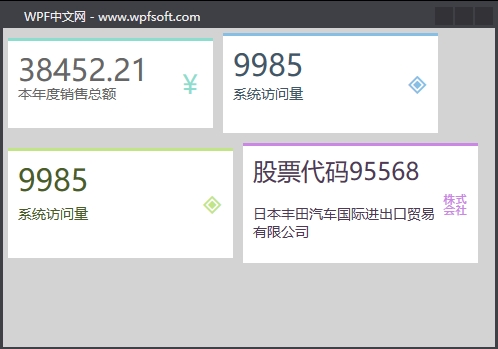
而且,Widget中的Value、Title、Icon三个属性还支持绑定功能,在本例中是直接赋值。关于依赖属性的初步了解,我们就先介绍到这里,下一讲,我们将更深入一些,去了解关于依赖属性的回调函数的用法。
当前课程源码下载:(注明:本站所有源代码请按标题搜索)
文件名:083-《DependencyProperty定义与使用》-源代码.rar
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1yu-q4tUtl0poLVgmcMfgBA
提取码:wpff
——重庆教主 2023年10月26日
首先我们介绍一下WPF的依赖属性系统,它是指WPF提供的一组服务,专门用来扩展WPF的属性功能,而受到这些服务支持的属性就称为依赖属性。
WPF的依赖属性系统对于开发者而言,几乎是感知不到的,它通过DependencyProperty类型的一些静态方法成员,提供一系列注册依赖属性或附加属性的功能,让我们可以向依赖属性系统注册属于我们自己写的依赖属性。
为了对比CLR普通属性与WPF的依赖属性的区别,直观的认知两者的概念,我们先来看看普通属性的定义
一、普通属性的定义
private int length = 0;
public int Length
{
get { return length; }
set { length = value; }
}
CLR普通属性的本质是在内部定义了一个私有字段,然后通过属性包装器将内部私有定段公开出来,get表示读出私有字段的值,set表示写入值到私有字段。假如WPF控件上的某个属性就是这类的普通属性,那么我们要更新这个属性的值,就只能赋值,用不能采用WPF的绑定方式了,因为只有依赖属性才支持绑定。
二、依赖属性的定义
在C#后端的类型中,输入:propdp,然后按下tab键,VS会自动帮我们输入以下代码:
public int MyProperty
{
get { return (int)GetValue(MyPropertyProperty); }
set { SetValue(MyPropertyProperty, value); }
}
// Using a DependencyProperty as the backing store for MyProperty.
// This enables animation, styling, binding, etc...
public static readonly DependencyProperty MyPropertyProperty =
DependencyProperty.Register("MyProperty", typeof(int), typeof(ownerclass), new PropertyMetadata(0));
我们来一一分析一下上述代码。
首先是MyPropertyProperty成员,它被声明为DependencyProperty 类型,且用DependencyProperty的Register方法注册,而在注册的时候,传入了4个参数。
第一个参数“MyProperty”:这个MyProperty其实是一个类似普通属性包装器的名字。经过依赖属性系统注册后,将来MyProperty就代表了MyPropertyProperty依赖属性。
第二个参数typeof(int):表示这个MyPropertyProperty的数据类型,也就是我们在使用MyProperty时的数据类型,这里被声明成int型。注意这里要求传入数据类型的反射。
第三个参数typeof(ownerclass):表示当前这个MyPropertyProperty依赖属性是属于哪个类的,一般填写当前这个类型。
第四个参数new PropertyMetadata(0):表示传入一个PropertyMetadata属性元数据。这个PropertyMetadata定义了MyPropertyProperty依赖属性的默认值和回调函数。回调函数就是当属性值发生改变时要执行的逻辑代码。
其次是MyProperty成员,它由CLR属性包装器实现get和set,并且使用了GetValue 和 SetValue成员去读出和写入MyPropertyProperty依赖属性。
咦?哪儿来的GetValue和SetValue?
在讲解WPF的基类时,我们曾经分享过DependencyObject类。这个类就定义了GetValue和SetValue,分别表示获取某个依赖属性的值和写入一个值到某个依赖属性。结论,我们要在某个类中自定义一个依赖属性,那么这个类一定要继承DependencyObject基类。
在了解依赖属性的概念和定义之后,我们就可以正式地去定义并使用它。下一节,我们将以一个实例来说明WPF的依赖属性用法。
——重庆教主 2023年10月25日
 WPF中文网
WPF中文网